|
Diamond
What
is diamond?
What is synthetic diamond?
What is the ways to synthesize diamond?
What is the characteristic of different synthetic
ways?
What ways does SUKAN adopt to synthesize diamond?
What is synthetic single crystal diamond?
What is the atomic structure of Synthetic Single
Crystal Diamond?
How is diamond size measured?
What is the standard to classify the quality of diamond?
What is the application of different standard diamond?
What is coated diamond?
Why are some ultra-hard grits metal coated?
What is PCD ( Polycrystalline Diamond)
What are the main applications for PCD?
What is diamond Micron powder?
What is the application for diamond Micron powder?
 What is diamond?
What is diamond?
A natural and synthetic
mineral composed of carbon atoms in a specific crystalline structure.
it is the physically hardest substance known and is now widely
used as an abrasive in high productivity tools in industry.
Diamond also has remarkable physical
properties such as:
Density (g/cm3) 3.52
Compressive strength (GPa) 8.68
Fracture toughness (MPam1/2) 3.40
Knoop hardness (GPa) 57 - 104
Young's modulus [GPa] 1141
Thermal expansion [10-6K-1] 1.5 - 4.8
Thermal conductivity [Wm-1K-1] 500 ¨C 2000
Wear coefficient 2.14 - 5.49
 What is synthetic diamond?
What is synthetic diamond?
Synthetic diamond can be synthesized using techniques, which emulate
the natural geological growth of diamond. This involves using
high pressure/high temperature (HPHT) synthesis process, which
converts the soft graphite carbon into the very hard crystalline
form of carbon - diamond (crystallization) or direct conversion
using explosives to generate short duration pressure and temperature
shock waves. Various industries take advantage of diamonds remarkable
physical properties. Principal mechanical applications are sawing,
drilling, grinding, cutting, lapping and polishing, truing.
 What is the ways to synthesize diamond?
What is the ways to synthesize diamond?
There are many ways to synthesize diamond, but only a few technologies
are adopted in Ultra-hard Materials industry. Synthetic diamond
can be produced through high temperature and high pressure or
made through its growth on inferior stable condition. The technology
by high temperature and high pressure can be divided into two
kinds: one is to synthesize diamond through stable pressure with
catalyst and the other is to produce diamond directly. The technology
to make diamond on inferior stable condition of diamond can be
classified to two kinds: one is that diamond is produced by its
growth in thin film shape on low pressure, and the other is that
diamond is synthesized on ordinary pressure and high temperature.
 What is the characteristic of different
synthetic ways?
What is the characteristic of different
synthetic ways?
The technology of producing diamond on stable pressure with catalyst
is that: on condition of thermodynamic stability of diamond, synthetic
diamond is produced through high temperature and high pressure
(by belt-type press or cubic press) with graphite as raw materials
and metal/alloy as catalyst. Most of ultra-hard material companies
(about 90%) adopt this way to produce synthetic diamond.
The technology of producing diamond directly through stable pressure
does not use catalyst, but it needs higher pressure and temperature
and thus needs better press, so it is not widely adopted in trade.
The technology of producing synthetic diamond on high pressure
and temperature realized by detonator explosion can produce micron
diamond crystal which is often imperfect and brittle. This technology
does not need expensive equipment and can realize high productivity,
but it is difficult to control temperature.
 What way does SUKAN adopt to synthesize
diamond?
What way does SUKAN adopt to synthesize
diamond?
SUKAN synthetic diamond is produced through stable
pressure with catalyst by belt type press and cubic press with
sheet graphite or powder graphite as material.
SUKAN RSD diamonds, produced with best raw materials
by belt type press, reach the highest level of quality standard.
Their best characteristics, including low impurities, improved
shape and color, excellent toughness index and thermal toughness
index, make them especially suitable for High Temperature Sintering.
SUKAN RBD diamonds are produced by cubic press.
They have similar properties with RSD series, thus provide an
economical choose of high grade diamond grit, and it is ideal
for low temperature sintering.
SUKAN RMD diamonds are medium quality diamond grits with
a wide range of usage and good performance in each particular
application, including drilling, sawing and grinding.
SUKAN RRB diamonds have superior bond retention
for their sharp shape, and are self-sharpening for their friability.
They are suitable for grinding and polishing non-ferrous materials.
 What is synthetic single crystal
diamond?
What is synthetic single crystal
diamond?

Synthetic single crystal diamond
is manufactured for industrial applications. It¡¯s produced by
high pressure / high temperature (HPHT) synthesis process and
strictly controlled crystal growth conditions. Repeatable physical
characteristics and dimensional consistency are the notable features
of synthetic single crystal diamond. For example, SUKAN offers
various series of synthetic single crystal diamond such as RSD/RBD/RMD/RRB
series. To know the detail the products, please feel free to view
the products column in our website.
 What
is the atomic structure of Synthetic Single Crystal Diamond?
What
is the atomic structure of Synthetic Single Crystal Diamond?
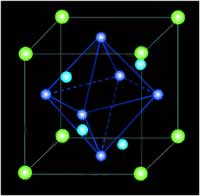
Synthetic
single crystal diamond has an identical physical structure to
that of natural single crystal diamond. The basic diamond atomic
structure, described by its unit cell, can be pictured as a face-centered
cube (as shown above) with a carbon atom in the middle of each
face and four more atoms arranged diagonally opposite each other
in pairs, with the upper plane offset at a right angle to the
lower plane. Unlike graphite, the individual planes are not flat
but corrugated. In diamond, each carbon atom is connected to four
other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. In the simplest case, these
four atoms form a perfect tetrahedron. Due to covalent bonding
between the atoms there are no free electrons and synthetic diamond
is normally not electrically conducting. In the case for synthetic
diamond, one or more of the carbon atoms might be replaced (or
substituted) with nitrogen atoms, giving the diamond a yellow
color.
 How is diamond grit measured?
How is diamond grit measured?
Diamond abrasives are traditionally sold in US mesh size ranges,
these mesh sizes are defined by the mesh size of sieves used to
separate the diamond particles. The sieve sizes are graduated
and defined by the number of lines per inch of each sieve e.g.
50 lines per inch or 20 lines per inch. The diamond is then sold
in overlapping mesh size ranges. This means for example in a sample
of 40/50 US mesh diamond most of the material would fall between
the 40 mesh and the 50 mesh sieve. International standards permit
that a small amount of oversize and undersize material is permitted,
but this is usually no more than 2-4%.
 What is the standard to classify the quality
of diamond?
What is the standard to classify the quality
of diamond?
There are a few kinds of criterions to classify the quality of
diamond, including crystal shape, strength, impact toughness,
thermal stability, etc. So diamond always is classified into a
few series according to their characteristics, for example, SUKAN
diamond can be classified into RSD, RBD, RMD and RRB series.
 What is the application of different standard
diamond?
What is the application of different standard
diamond?
Diamond grit always is applied in different use area according
to its quality characteristic. The diamond series from SUKAN can
make good example to explain it. SUKAN RSD series, because of
their low impurities, improved shape and color, excellent toughness
index and thermal toughness index, are especially suitable for
high temperature sintering and made of geological drilling or
various saws. SUKAN RBD series are good for sawing and drilling
application and they are ideal for low temperature sintering to
be made of tools to machining granite, concrete, tough marble.
SUKAN RMD series are medium quality diamond grits and are suitable
for wide range of application such as grinding and sawing of glass,
marble, rock. SUKAN RRB diamonds have superior bond retention
for their sharp shape, and are self-sharpening for their friability.
They are suitable for grinding and polishing non-ferrous materials.
 What is coated diamond?
What is coated diamond?
Coated diamond refers to the diamond with metal coverage on the
crystals, and coated diamond is highly adhesive in bond system
and better thermal stable. Thus the tools life and processing
cost are remarkably improved. SUKAN can offer various coated diamond
with upon request.
 Why are some ultra-hard grits metal
coated?
Why are some ultra-hard grits metal
coated?
Metal coating can be classified two kinds. One is Metal cladding
comprising a thick layer of typically nickel or copper which can
be up to 60% of the total particle weight. These clad particles
are generally used in resin bonded tools such as grinding wheels.
The effect of the cladding is to improve the retention of the
abrasive in the bond and help dissipate the heat generated during
grinding and hence improve performance of the tool. Another is
Metal coating comprises a thin layer of metal, such as titanium.
When used in bonds which use high temperatures during their manufacture
such as some metal and vitrified bond systems these coatings can
improve particle retention and protects the diamond during manufacturing
of the tool/segment.
 What is PCD ( Polycrystalline Diamond)
What is PCD ( Polycrystalline Diamond)

PCD
refers specifically to diamond particles which have been sintered
together into a coherent structure using a chemo-mechanical binder
and high-pressure, high-temperature conditions similar to those
used in single crystal diamond synthesis. These sintered PCD materials
have extensive range of uses, most notably for cutting tools machining
non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials and for wear parts.
An advantage of these materials is that their structure and composition
can be engineered to have properties tailored to specific applications
and operations. SUKAN can offer PCD specified by customers, and
PCD with metal layer formed on the surface available upon requests.
 What are the main applications of PCD?
What are the main applications of PCD?
The best application of PCD can be classified three kinds of area
as below:
(1) Cutting non-ferrous metals and alloys.
(2) Cutting wood particle board (particularly medium density fibreboard
- MDF, and chipboard in the furniture industry).
(3) Non-cutting applications such as wear-parts.
 What is diamond Micron powder?
What is diamond Micron powder?
Diamond micron powder refers to very fine abrasives made of diamond
crystal. They are used, for instance, in precision machining and
polishing applications. Applications include the use of micron
diamond as loose powder, in for instance polishing, or in bonded
tools, such as grinding wheels. Sukan can supply a variety of
diamond Micro powder product.
 What
is the application for diamond Micron powder?
What
is the application for diamond Micron powder?
Diamond Micron powder is used extensively in electronics, aviation
and space flight, optical instrument, glass, ceramics, petroleum,
geology and other fields. Diamond Micron powder is the best material
for grinding and polishing hard alloy, ceramics, gem stones and
optical glass.
|